This tutorial will help you to how to install Apache Tomcat 10 on Debian 10 Buster Linux system.
Prerequisites
A running Debian 10 system with sudo privileged account shell access. You can get cheaper instances from DigitalOcean hosting.
Step 1 – Install Java
Tomcat 10 required JRE 8 or higher version installed on your system. If your system doesn’t have JRE installed, Use the following commands to install OpenJDK to fulfil the requirements. Check the current active Java version:
Step 2 – Create Tomcat User
It is good to have a dedicated user account for running a Tomcat server. To create a new user with the name “tomcat”, which is recommended for security purposes mainly for production deployments. To create a new account, type: The above command will create a user and group with the name “tomcat” in your system.
Step 3 – Install Tomcat on Debian 10
The Apache Tomcat development team releases the latest version of Tomcat from time to time. So it will be good check download latest Tomcat version from the official download server. Use the below command to download Tomcat 10. After downloading the archive file, extract the file under the tomcat home directory /opt/tomcat with skipping parent folder. Next, set the proper file permissions. You have now the latest Tomcat application on your system.
Step 4 – Create Tomcat User
Now, configure your tomcat with user accounts to secure access of admin/manager pages. To do this, edit conf/tomcat-users.xml file in your editor and paste the following code inside
Step 5 – Enable Remote Tomcat Access
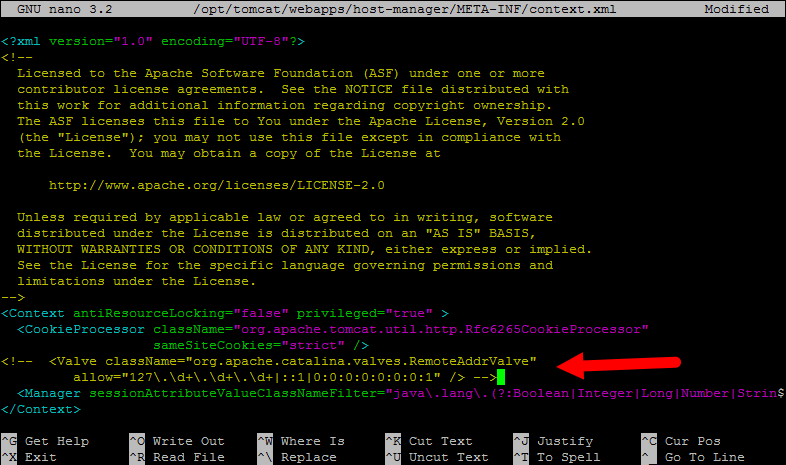
The default Tomcat manager and host-manager applications are accessible for localhost only. To allow access to these pages from the remote system, you need to modify the following configuration files. You can either allow specific remote system or allow all. Edit the context.xml file for manager and host manager application: Comment out the section added for IP address restriction to allow connections from anywhere. Also, edit the context.xml for the host-manager interface and comment on the similar section as above.
Save all files and close them.
Step 6 – Create a Tomcat Systemd Unit File
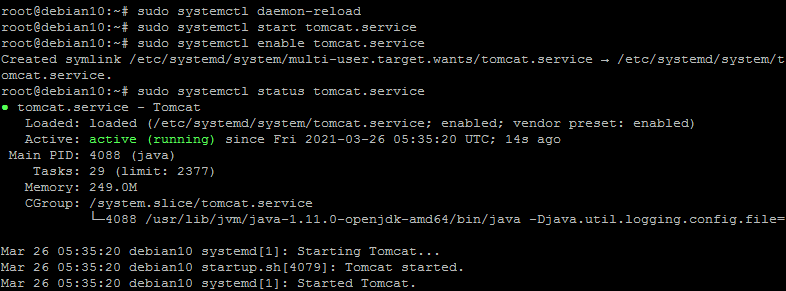
Tomcat provides bash scripts to start, stop service. But, to make it simple, create a start-up script to manage Tomcat as systemd service. Let’s create a tomcat.service file with the following content: Reload the systemd daemon service to load newly create files. Now, start the Tomcat application for the first time. Next, enable the tomcat service to auto-start for subsequent system boots. This is more important for the production deployments. As of now, the tomcat application is running on your system. You can verify the service status by executing the command as below. Make sure the status is showing “active (running)“.
That’s it. You have successfully configured Tomcat 10 on your Debian system.
Step 7 – Access the Tomcat Web Interface
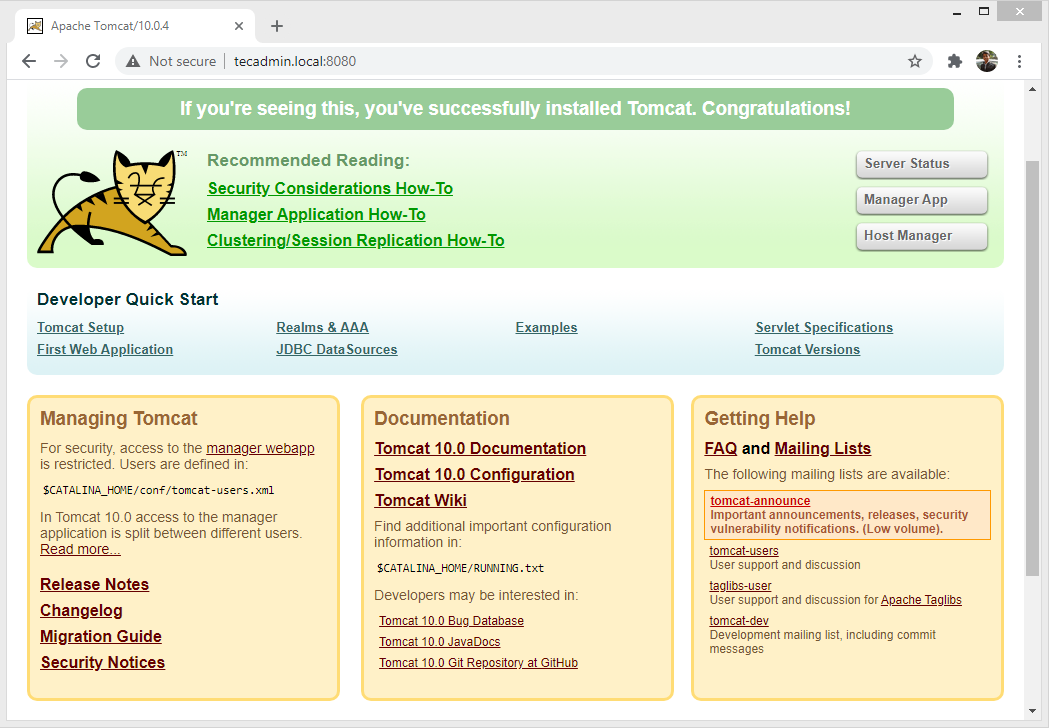
The default Tomcat server runs on port 8080. As you have configured Tomcat on your system, you can access the web interface from your system. You can access tomcat interfaces by entering your server’s IP address or a domain name pointed to that server, followed by port 8080 in your browser: Change tecadmin.local with your server ip or domain or localhost. You will see the page like below:
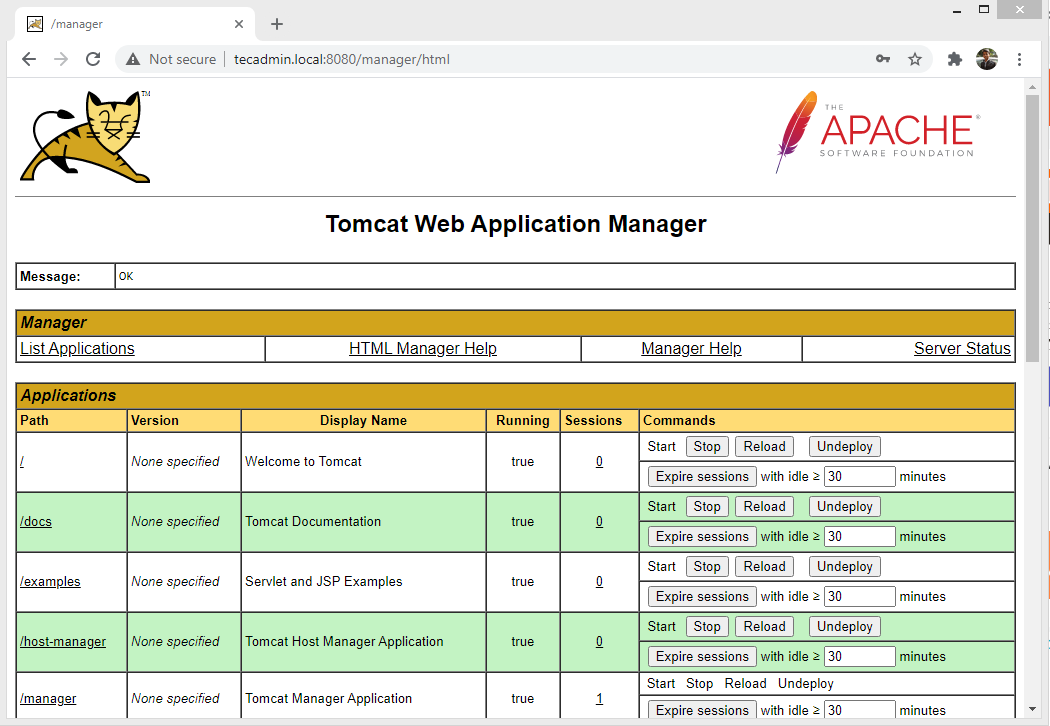
Tomcat Manager App is a web application packaged with the Tomcat server application. The Manager interface provides us with the basic functionality we need to manage our deployed web applications. Click Manager App button home page or directly type /manager in browser url of main Tomcat server to access it.
Tomcat Host Manager App is another web application packaged with Tomcat server application. Which is used to creates/removes Virtual Hosts within the Tomcat service. A Virtual Host allows you to define multiple hostnames on a single server. Click Host Manager button home page or directly type /host-manager url in main Tomcat server to access it.
Conclusion
Congratulations, You have a running Tomcat server on a Debian system. You can deploy a Java-based application using a tomcat server. You may also need to create Virtualhosts in Tomcat or Secure your Tomcat applications with Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate.