In this article, we will see how to install and use VirtualBox 7.0 on Fedora 36/35. The VirtualBox 7.0 package is not available for Fedora 34 and older versions but still you can install VirtualBox 6.1 on that system.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that you have the following prerequisites: – A computer running Fedora- A minimum of 4 GB RAM- 10 GB free disk space- A host machine running any of the following operating systems: Windows, Linux, Mac OS X – Install VirtualBox and Extension Pack on Fedora. First of all, you should install the Development Tools required for building VirtualBox Linux kernel modules on Fedora along with a few additional packages. After installing the latest kernel and kernel headers, let’s reboot your system and start with the latest kernel.
Step 1: Configure RPM Repository
The VirtualBox development team provides an RPM repository for the installation. You simply need to configure this RPM repository on your system depending on your Fedora version. You can verify the repository file by viewing its content. Make sure that the repo file is created correctly.
Step 2: Install VirtualBox on Fedora
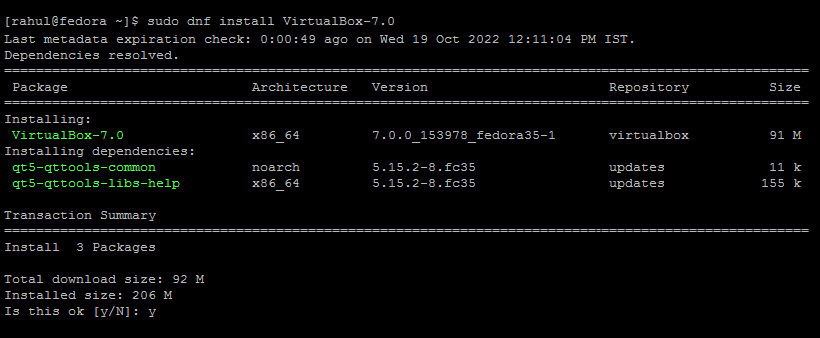
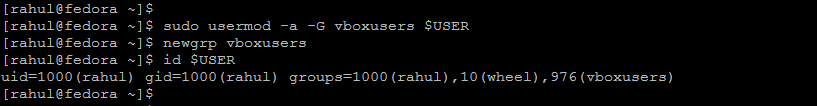
Use the following command to install VirtualBox using the DNF command-line tool. It will install the latest version of VirtualBox on your Fedora system. VirtualBox installation processes creates group vboxusers in your system. You should add your current user to this group, so you can get more permissions to manage Virtualbox from your account.
Step 3: Launch VirtualBox
You have successfully installed VirtualBox software on your fedora system. Now login to the Ubuntu desktop to start using VirtualBox. Where you can create virtual machines for different operating systems. Search the term “VirtualBox” under the applications and you will see the launcher icon as shown below: Click the launcher icon to start VirtualBox on your Ubuntu system. You can use the New button to start creating a new virtual machine. Under the preferences, you can customize the default options. Import and Export buttons are used to migrate existing virtual machines from one system to another systems.
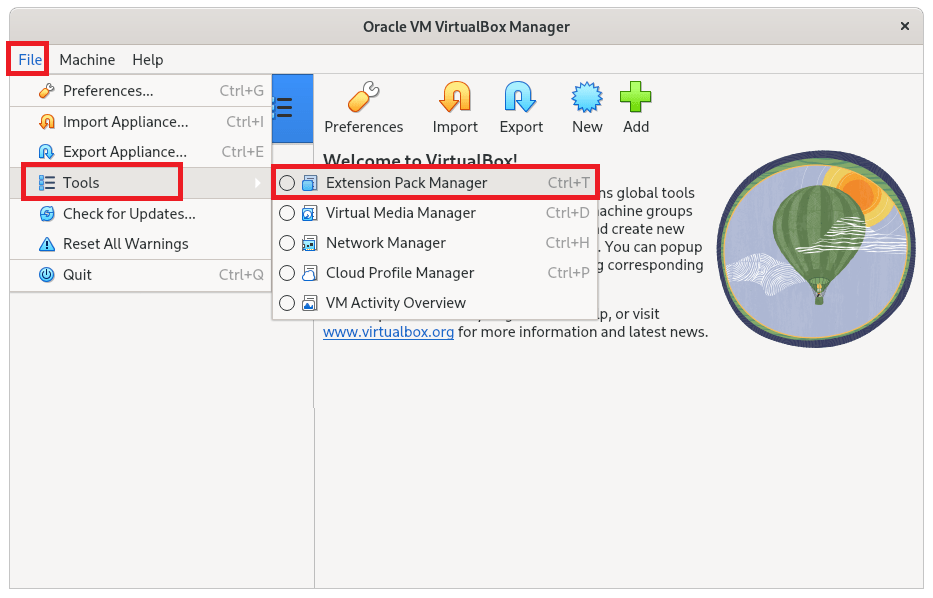
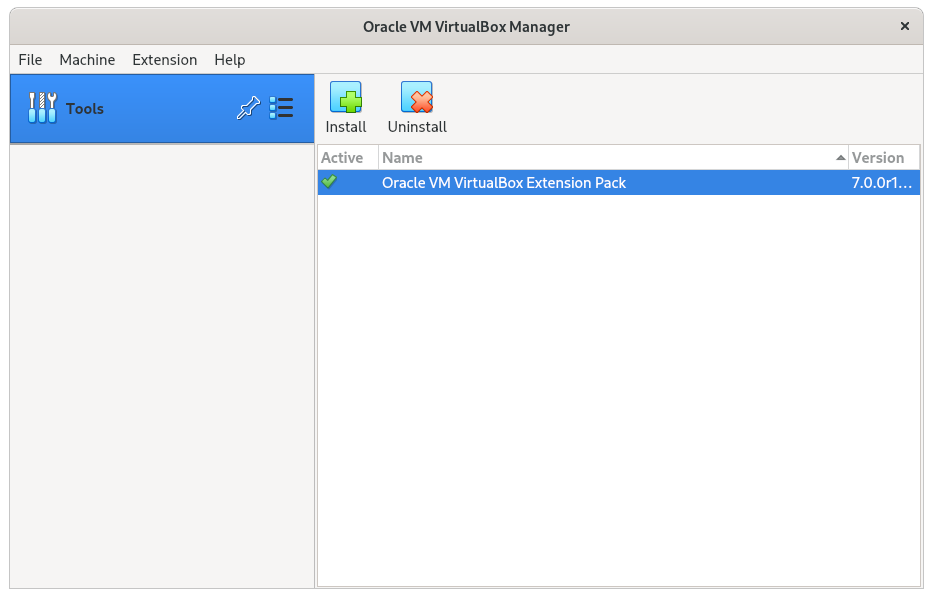
Step 4: Install VirtualBox Extension Pack
The VirtualBox Extension Pack is an optional component that allows you to enhance the functionality of VirtualBox. It provides you with additional features like improved network performance, USB device support, and many others. To install the VirtualBox Extension Pack, follow the below steps: The above command will install the VirtualBox extension pack on Fedora.
Conclusion
VirtualBox is powerful virtualization software that can be used to run virtual machines on a computer. In this article, you learned how to install VirtualBox on Fedora, a free and open-source Linux operating system. Now, you can install and run different operating systems like Windows, Linux, and many more inside VirtualBox. If you encounter any issues during the installation or use of VirtualBox, feel free to comment below. We’ll be happy to help you out.