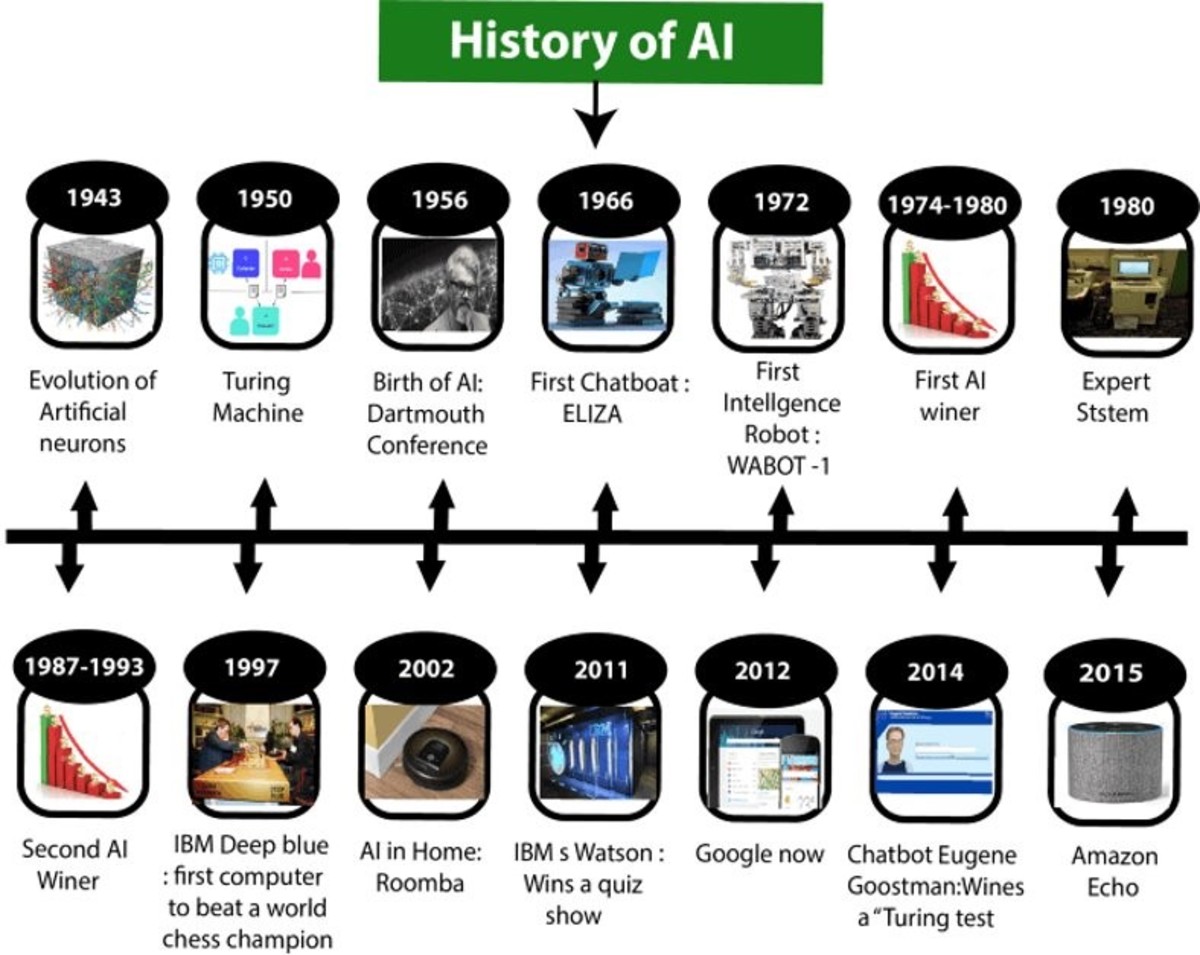
History of Artificial Intelligence
So let us start from the origin of artificial intelligence. According to Adrienne Mayor, a research scholar in the department of classics in the School of Humanities and Sciences, the history of artificial intelligence has its roots in Greek mythology. The myth states that Hephaestus, a Greek god of invention and mythology, was the first inventor of artificial intelligence when he built Talos, a giant bronze man. Talos was commissioned to protect the island of Crete from invaders sent by Zeus, the king of Greek gods. He was deployed to throw boulders at the ship of enemies and would complete three rounds around the island daily. In the 20th-century modern world was familiarized with the topic of artificial intelligence. The period between 1940 and 1960 is regarded as the time when the world experienced significant technological development. At the beginning of 1950, John Von Neumann and Alan Turing became the founding fathers of AI when they made a transition from decimal logic (numbers from 0 to 9) to binary logic (numbers 0 and 1). The breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence came when Alan Turing devised his famous Turing Test (However it does not appear to qualify the norms of AI for many experts) which checks if the machine can think like humans or not. The structure of the test was as follows: Interrogator: Are you a machine? Computer: No. Interrogator: Then multiply 25146962 by 15963248. Computer: (Takes a long pause and gives a wrong answer.) In this game, if the interrogator is unable to distinguish between the human and the machine, then the machine passes the test. Eliza was the first chatterbox to attempt the Turing Test and its creator, Eugene Goostman, won the competition, convincing 29% of the judges that Eliza was a human. The term artificial intelligence was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 during the Dartmouth conference organized by John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky, which is considered the foundation of the discipline. It is worth noting this was less a conference and more of a workshop. It was attended by only six people, including McCarthy and Minsky. Herbert Simon, economist, and sociologist suggested in 1957 that AI would be able to beat humans in chess in 10 years. However, during that time, AI entered its first winter and his prediction came true after 30 years. In May 1997, IBM Deep Blue became the first computer to beat a human, the world chess champion, Garry Kasparov. Kasparov stated that one of the major causes that weighed against his victory was that he was denied access to the previous games of IBM Deep Blue in contrast to the computer which might have studied 100 games of him. Kasparov also suggested that he saw deep intelligence and creativity in the second game, and suspected chances of human intervention but it was denied by IBM. Kasparov asked for the log files of the computer but after being denied earlier, the files were published on the internet by IBM. The operations of the computer were based on a brute force algorithm, where the computer would analyze each move and then evaluate the next possible moves. Although these types of operations were never supported, they remained a symbolic breakthrough in the history of AI. This was the first time when humans realized that AI can beat human intelligence. But many experts believed that Deep Blue had in reality only managed to treat a very limited perimeter and was far from the complexity of the real game.
Recent AI Development
Since 2010, access to high-volume data and the discovery of high-efficiency processors that accelerate calculating power have brought a new bloom in the field of AI. Amongst the machine learning techniques, the most promising technique is deep learning, which is used for image and voice recognition and has a wide variety of real-world uses.
Is the Future of AI Safe for Humanity?
Many scientists say answering this question requires weighing multiple pros and cons, as well as considering unknown factors. On the beneficial side, artificial intelligence eliminates the necessity for humans to perform tedious tasks. It reduces the chances of error as compared to that of humans. Some uses of artificial intelligence involve using AI robots for risky activities. AI robots are used in crash tests and the mining of coal and oil. AI robots are also deployed in nuclear power plants, which can help to minimize the effects of radiation and control the fire during the time of accidents. The development of technologies like Siri by Apple, Cortana by Microsoft, and Google’s OK Google have made human life much easier. Voice assistance devices can be especially helpful for handicapped persons who want to live independently. AI can be used in the healthcare sector in the development of new drugs by identifying the potential molecules and leveraging a large volume of data. Artificial intelligence software’s been used in disease detection where it is useful in detecting the disease-affected areas, helping the doctors to be specific about further procedures. Due to its faster decision-making, AI has been used in creating recreational gaming software for humans and for doing hard calculations precisely. One of the unproven contentions about AI is that it may turn evil in the future. Usually, such articles are accompanied by evil-looking robots to lure people into believing in them. In reality, the major worry of many researchers who believe that AI can be harmful to humans is that its goals will not be aligned with ours. They believe that intelligence enables control and if AI becomes smarter than humans it could be harmful to the human race. There is also concern that humans are getting addicted to artificial intelligence software, which could be harmful to future generations. Development in the field of artificial intelligence is also leading to the scarcity of employment. Companies are developing technologies that can replace humans in work and most businesses are preferring the use of AI technologies for their work as it increases the accuracy and makes the computation faster. But some companies understand that while AI automation can replace minimum qualified individuals, it will take a long time for AI robots to replace humans in high-capacity positions. Adding to the hysteria, business magnate Elon Musk has also warned that there will be a time when AI robots will take over humans.
Preparing for a Shared Future
The effect of artificial intelligence on the human race depends on us only. Should we develop lethal weapons or technology to improve mankind? Do we prefer new jobs replacing old ones or a society where everyone is living a life of leisure and enjoying machine-generated wealth? Do we prefer AI for satisfying personal motives or using it for social good? Finally, we need to be empowered by AI and not overpowered by it. The future of AI with humans is dependent on how we utilize it. If utilized properly, it could be one of the greatest boons for humanity. This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and is not meant to substitute for formal and individualized advice from a qualified professional. © 2022 Shantanu Singh Verma